Disease of the Month: AIDS
“Putting Ourselves to the Test: Achieving Equity to End HIV” -Theme of the year 2022
Introduction:
HIV/AIDS is one of the top 10 cause of mortality. It is a chronic, epidemic disease caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a virus that infect WBC’s CD4 T-cell of the immune system.
HIV, a type of retrovirus that isn't spread through the air, water or insect bites. It spreads only by having sex with an infected partner, contact with infected blood, by sharing needles from blood transfusions, during pregnancy or through breastfeeding
Every year 1st of December is marked as world AIDS day to encourage people to get rid of the disparities and inequities that create barriers to HIV testing, prevention, and access to HIV care
History of HIV:
It is assumed that HIV infection came from Simian immunodeficiency virus of chimpanzees (SIVcpz) in Central Africa. In the late 1800s, these chimpanzees were hunted for meat and came in contact with their infected blood. Over decades, HIV slowly spread across Africa and later into other parts of the world
Epidemiology:
~84.2M people are infected with HIV and ~40.1M people have died from AIDS-related illnesses since the start of the epidemic
In 2021, total ~38.4M people were living with HIV globally. Out of these, 36.7M were adults and 1.7M were children (<15 years old). ~1.5M newly infected people were identified and ~650 000 people died from AIDS-related illnesses
Symptoms:
HIV can occur in many phases and symptoms. These symptoms develop according to the progression of disease
1. Primary phase/Acute HIV, develops a flu-like illness within 2 to 4 weeks after the virus enters the body and it may last for a few wks.
2. Clinical latent infection (Chronic HIV), HIV is still present in the body However, many people may not have any symptoms or infections during this time
3. Symptomatic HIV infection, as the virus continues to multiply and destroy your immune cells the cells in the body that help fight off germs. Symptoms includes:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Diarrhoea
- Cough
- Pneumonia
- Headache
- Rashes
- Weight loss
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Shingles (herpes zoster)
- Muscle aches and joint pain,
- Sore throat
4. Progression to AIDS, when AIDS occurs, the immune system has been severely damaged and people will be more likely to develop diseases that wouldn't usually cause illness in a person with a healthy immune system Untreated, HIV usually turns into AIDS in about 8 to 10 years
Treatment:
Taking pills every day for life time, long-term toxicity and viral mutation cause by treatment are the unmet needs. So, there is a need to move into less frequently administered injectable HIV drugs
Till now, no effective cure for AIDS has been developed. Once people get HIV, they have it for life.
There are ~35 ART (antiretroviral therapy) available in the market that keeps HIV replication suppressed and allows immune system to strengthen and regain the capacity to fight off opportunistic infections. In 2021, ~28.7M people were reported to access ART that reduced AIDS deaths around the world.
Since 2016, WHO has recommended ‘Treat All strategy’. According to it, all people living with HIV will be provided lifelong ART. Apart from it, WHO also recommends a rapid ART initiation to all people living with HIV, including offering ART on the same day as diagnosis among those who are ready to start treatment
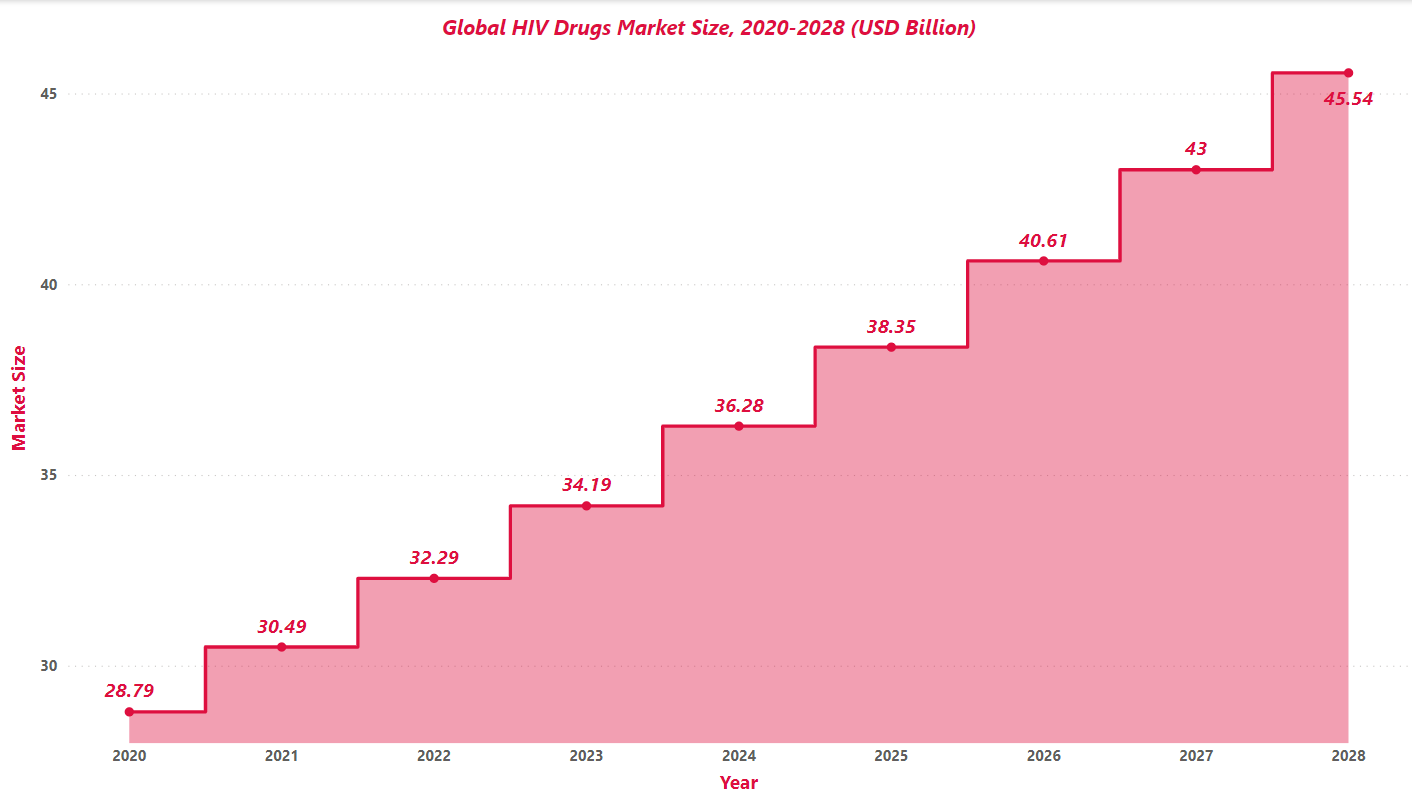
Market Share:
The global HIV drugs market is $28.79B in 2020, $30.49B in 2021 and $32.29 in 2022. In 2028 the market is expected to increase $45.54B at a CAGR of 5.9%.
Advancement:
Various HAART therapy (combination of three or more drugs) are under development to treat HIV. HAART stops the virus from making copies of itself in the body, reduce damage to the immune system caused by HIV and it may slow down the development and transmission of HIV. It is also called cART (combination antiretroviral therapy), or highly active antiretroviral therapy
Despite the current cART, HIV still remains to be an incurable disease
Apart from all these, researchers also evaluating “off-the-shelf” CAR-T cell therapy for long-term HIV remission without ART drugs. The first patient has been dosed in the Phase I/II study (NCT04648046) at the University of California to evaluate the safety and tolerability of anti-HIV duoCAR-T cells in adults living with HIV
Clinical Trial Analysis:
Based on G10 geography distribution, the interventional clinical trials are classified in the below mentioned graph in two groups based on its status, active (recruiting, active, not recruiting and not yet recruiting, enrolling by invitation) and inactive (withdrawn, suspended terminated, trials with unknow status). The interpretation showed that more no. of clinical trials being carried out in the US and the least number of trials are reported in India (as represented in the graph)
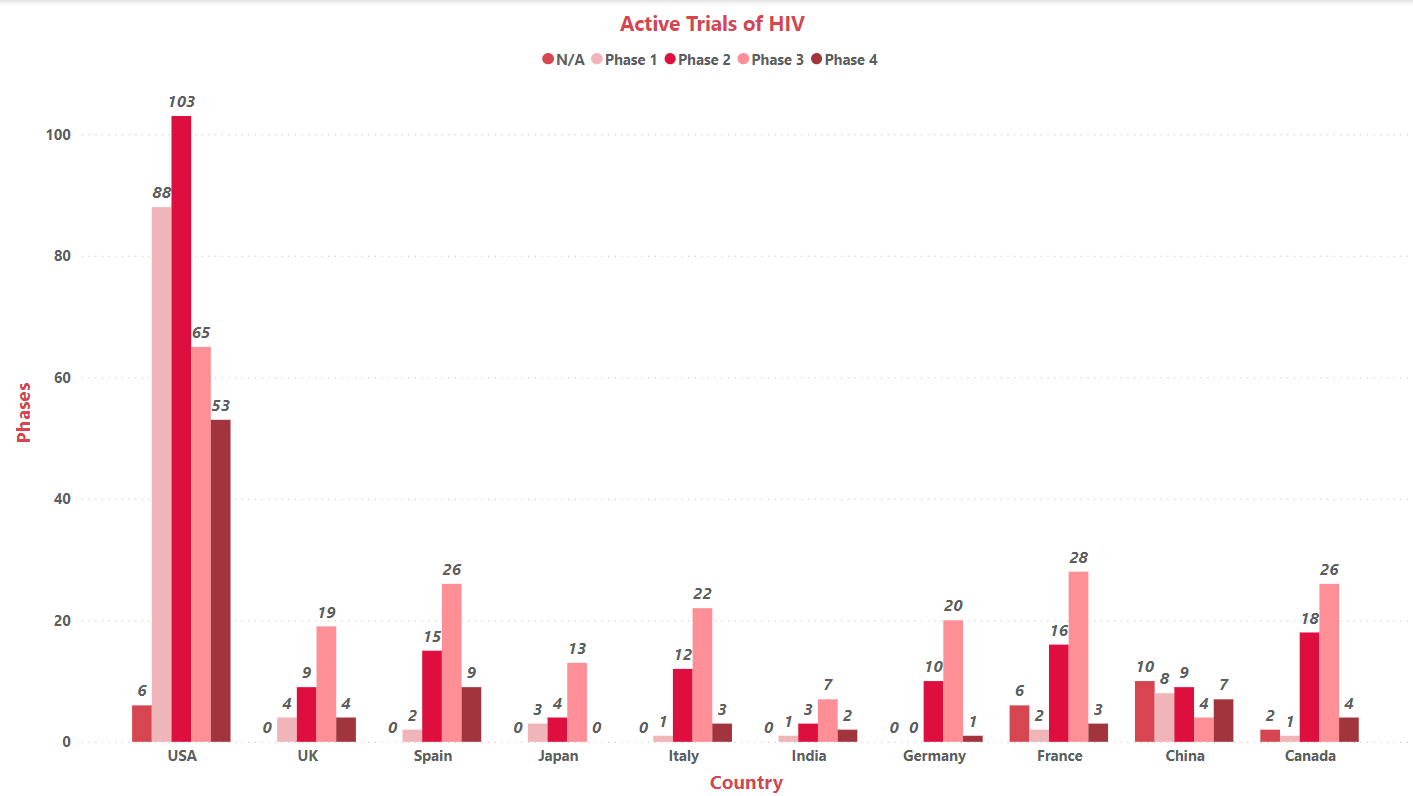
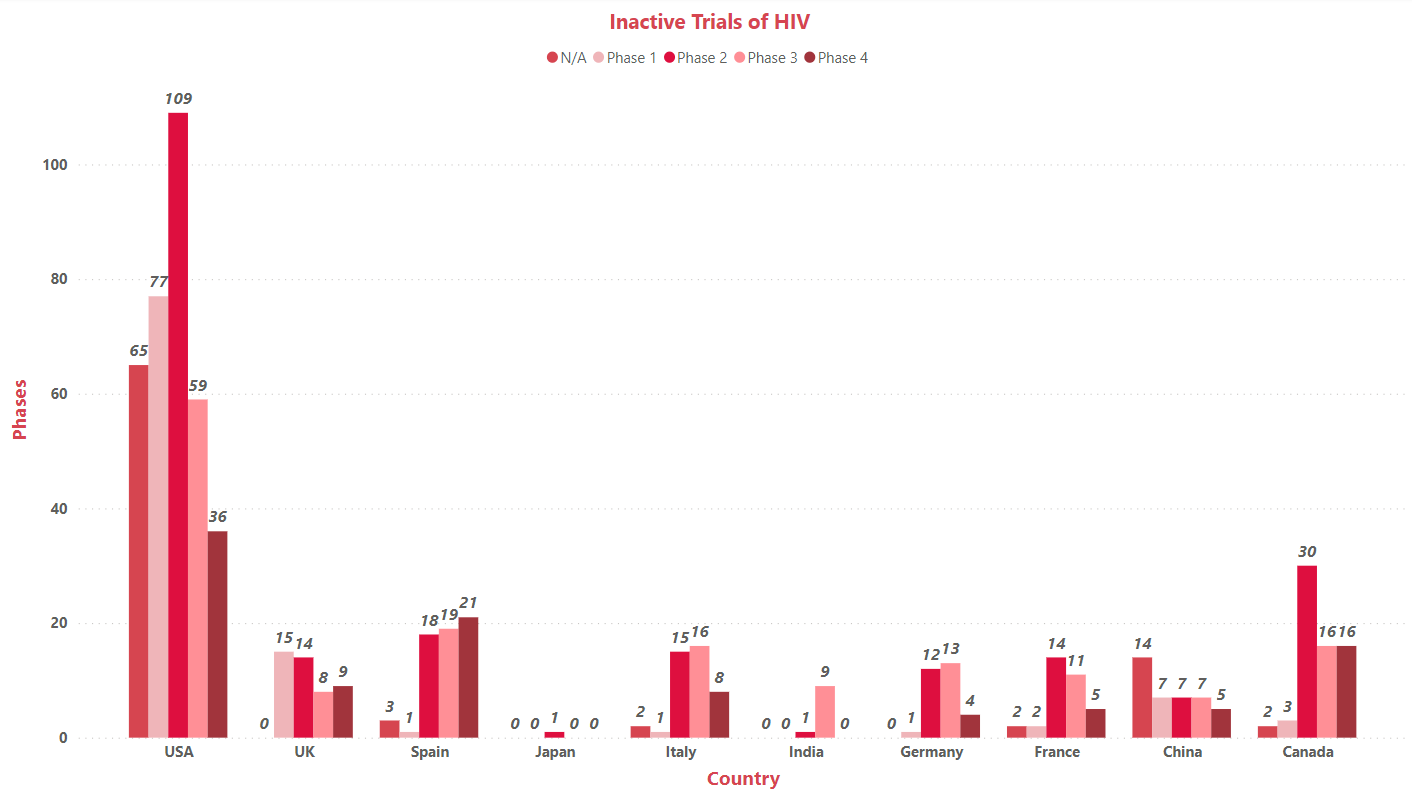
*This graphical interpretation is based on our point of view of the clinical data
Major Key Players:
The top key players having approved drugs for HIV in the global market include ViiV Healthcare, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck, GSK, BMS, Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim, Mylan Pharmaceuticals and others
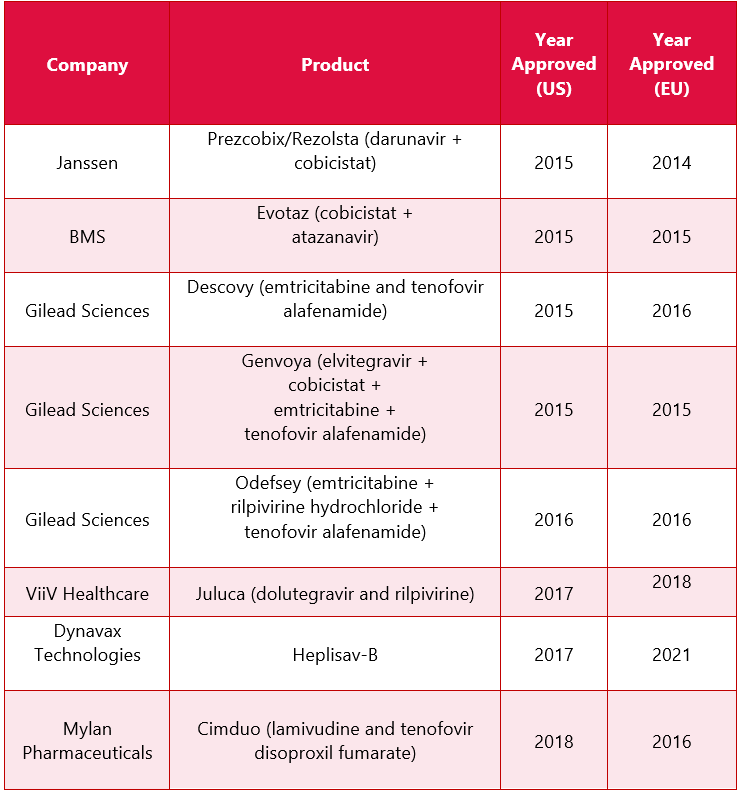
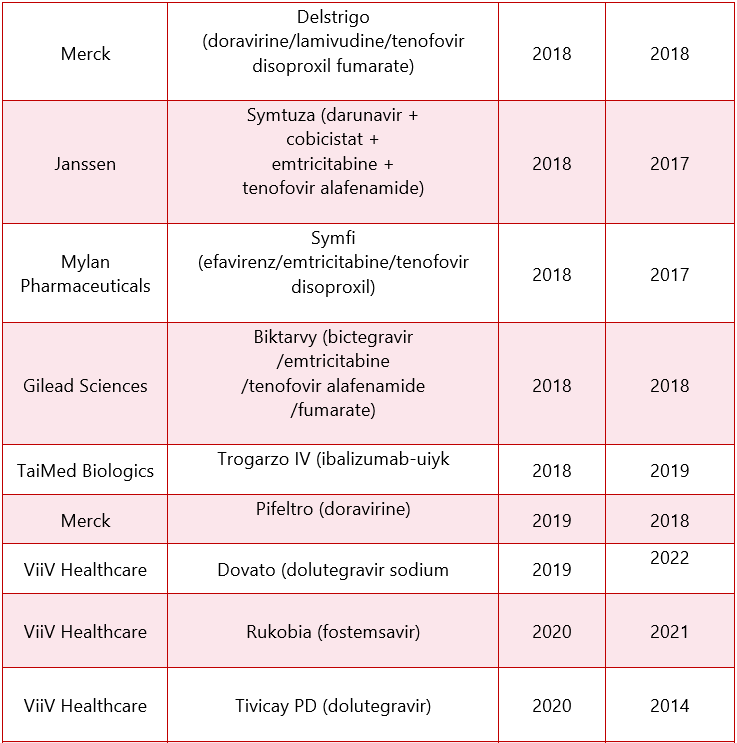
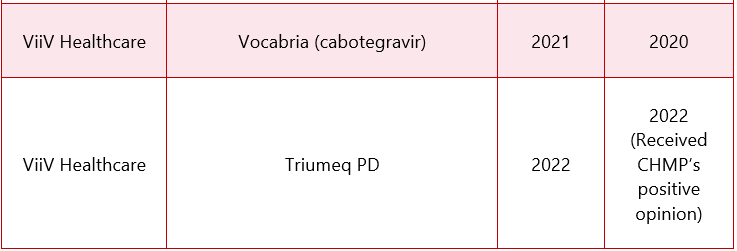
*The above mentioned table include the drugs which received approval after 2015
*Received only CHMP’s positive opinion, not approved yet
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of HIV includes 3 types of tests
Antibody Test: It detects HIV IgM and/or IgG antibodies The most rapid and self-test approved by the US FDA. It uses blood or saliva to detect HIV sooner. It take 23 to 90 days to detect HIV after exposure
Antigen/Antibody Test: It detects HIV p24 antigen as well as HIV immunoglobulin IgM and IgG and test for both HIV antibodies and antigens. It is recommended for testing done in labs, involves drawing blood from a vein. There is also a rapid antigen/antibody test that is done with blood from a finger stick. It detect HIV 18 to 45 days after exposure
Nucleic Acid Test: It detects HIV RNA and test if a person has HIV or actual virus present in the blood the health care provider will draw blood from your vein and send the sample to a lab for testing. It usually detects HIV in 10 to 33 days after exposure
References:
Related Post: Disease of the Month: Epilepsy | PharmaShots
Tags

Akanksha was a content writer at PharmaShots. She is interested in covering recent innovations from pharma & medtech industry. She covers news related to Product approvals, clinical trial results, and updates. She is passionate, meticulous, diligent, and inquisitive. She can be contacted at connect@pharmashots.com.